For precious and fragile artworks or artifacts, we use various visible and invisible light for "non-destructive testing" to understand their health condition. Light is a type of electromagnetic wave that travels and spreads through space in wave form.
Wavelength info based on eHanlin Smart Learning -High School Physics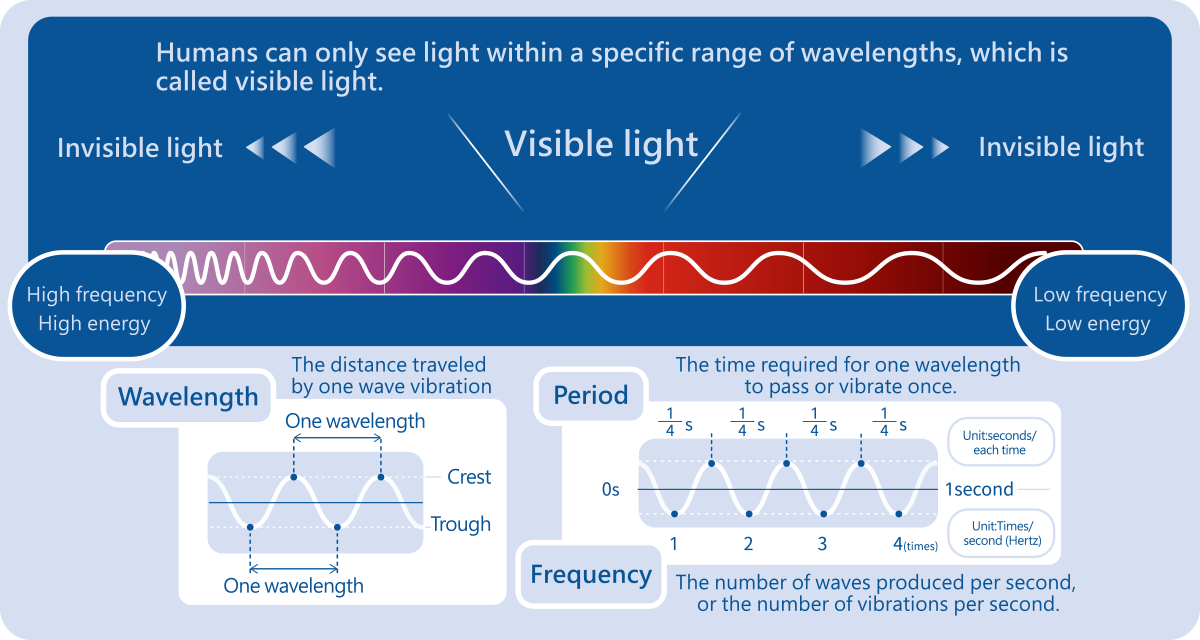
Let's See How These Types of Lights are Used in Our Daily Lives!
-

Ultraviolet (UV) Light
Wavelength: 10 nanometers to 400 nanometers
Although UV light is invisible to the naked eye, you can feel its presence. Especially in the summer, if you spend too much time outdoors, your skin will become dark or even red and swollen, as UV light has powerful energy that can stimulate melanin production in the skin, damage skin tissues, and even harm the eyes. Don't underestimate its power! -

Infrared (IR) Light
Wavelength: 750 nanometers to 100 micrometers
Infrared light is everywhere in our daily environment. For example, when we get close to a fireplace or a hot object, we feel warmth from the infrared light. Its characteristic is that it can be absorbed by the skin and converted into heat. Infrared light is also used in the remote controls for our TVs and air conditioners. -

Gamma Rays (γ-rays)
Wavelength: Below 0.01 nanometers
Compared to visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays, gamma rays have shorter wavelengths and higher energy. They can be used in medical examinations and treatments, but handling them is highly dangerous, so we must wear special protective clothing when dealing with gamma rays. -
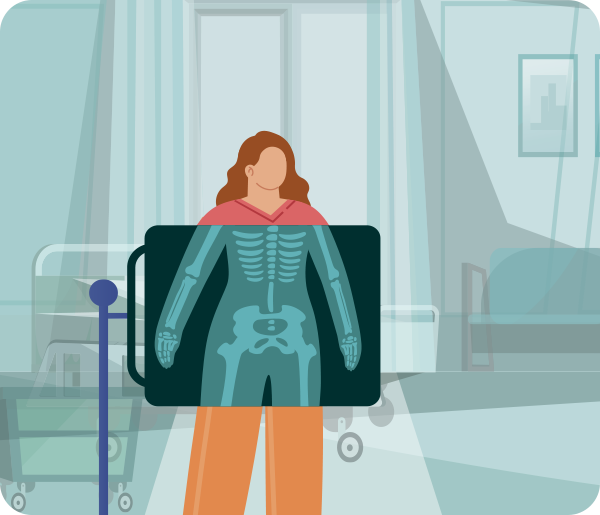
X-rays
Wavelength: 0.01 nanometers to 10 nanometers
X-rays have very short wavelengths, allowing them to penetrate through materials without causing damage. They are very suitable for inspecting the materials and structures of objects. In medicine, X-rays help doctors see inside the body to diagnose diseases more accurately and help patients recover sooner. -
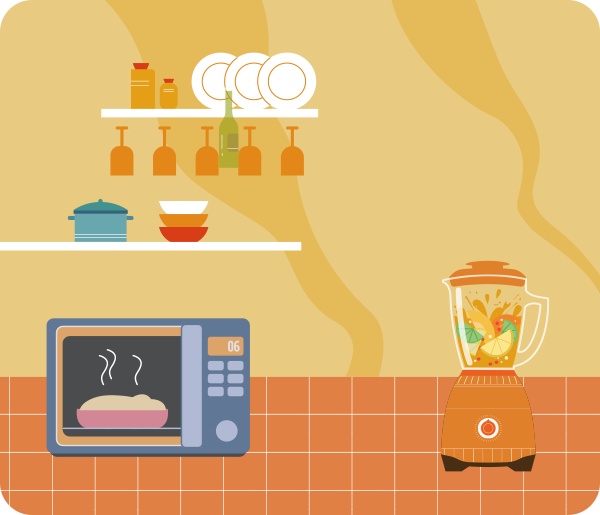

Microwaves
Wavelength: 1 millimeter to 1 meter
The most familiar application of microwaves is the microwave oven. It generates microwaves that rapidly agitate and collide water molecules in food, generating heat to cook the food. -
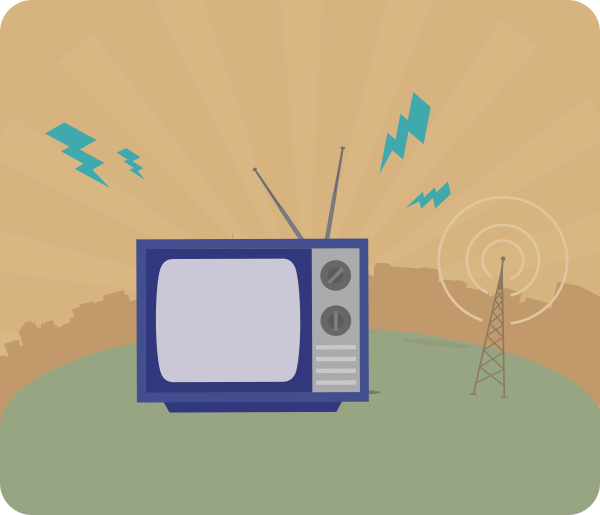

Radio Waves
Wavelength: 15 centimeters to 2 kilometers
Radio waves are commonly used for long-distance communication due to their characteristics of being difficult to block and having adjustable frequencies. Although we can't see radio waves, our phones, TVs, or radios transmit signals in the form of radio waves, which are then converted into audible sounds or visible images. -
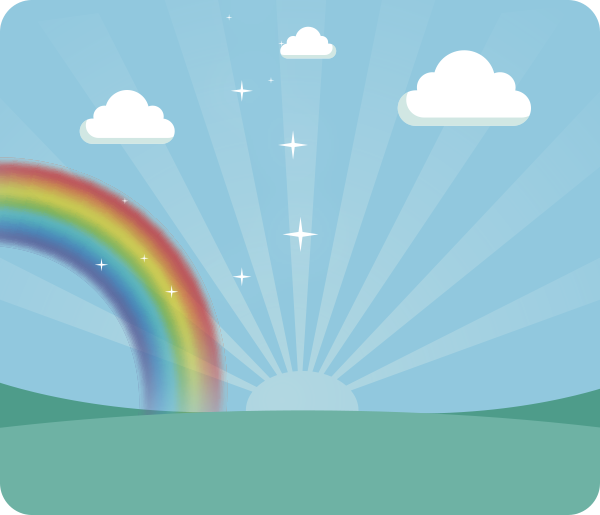

Visible Light
Wavelength: 400 nanometers to 750 nanometers
Visible light is the electromagnetic wave that humans can see. In daily life, most of the visible light comes from the sun, which is a natural light source. The artificial light we use indoors comes from artificial light sources. If we arrange light of various colors according to wavelength from largest to smallest, they are red light, orange light, yellow light, green light, blue light, indigo light, and violet light. There are no clear boundaries between these colors, forming a continuous spectrum of visible light. The color of light can be formed by mixing light of different wavelengths.