X: That Light
German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (1845-1923) discovered a mysterious ray while experimenting with cathode ray tubes. This ray was invisible to the naked eye but could penetrate through many substances. Röntgen used this ray to take the first-ever X-ray image of his wife's hand. At that time, the nature of this ray was not clear, so it was named X-ray.
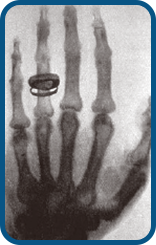


December 22, 1895
The world's first X-ray image
The world's first X-ray image

Röntgen
Because of the discovery of X-rays, Röntgen became the first physicist to win the Nobel Prize in 1901. His contributions continue to influence us all!
"Seeing Through" the Inner Secrets
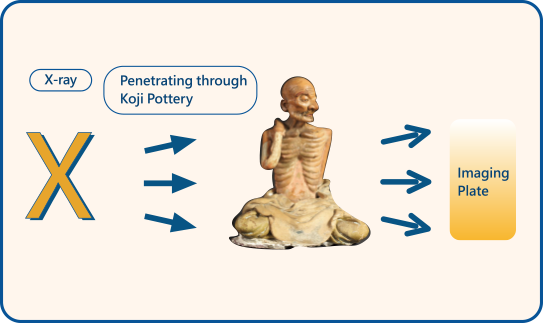
Through X-ray technology, we have the ability to "penetrate" the interior of the human body or objects without causing damage. In medicine, it can help doctors examine internal organs and bones. At airports, it can quickly check whether passengers' luggage contains prohibited items. In addition, X-rays can also reveal the internal structure and material information of artifacts, aiding in preservation and identification work.
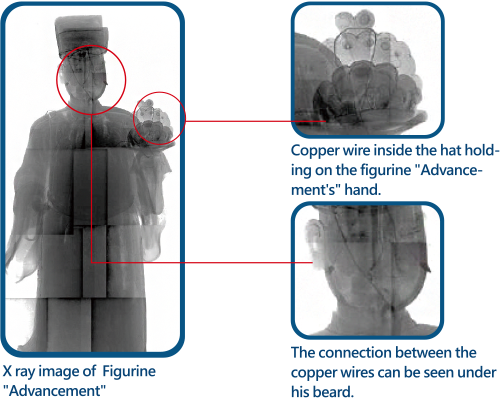
From numerous X-ray images of artifacts, researchers discovered five different processing techniques at the junctions of the dolls' heads and bodies. Based on the analysis of these techniques, we can tell whether it is an original work by Ye Wang, a later repair, or an imitation.
X-ray Machine Simulation Inspection
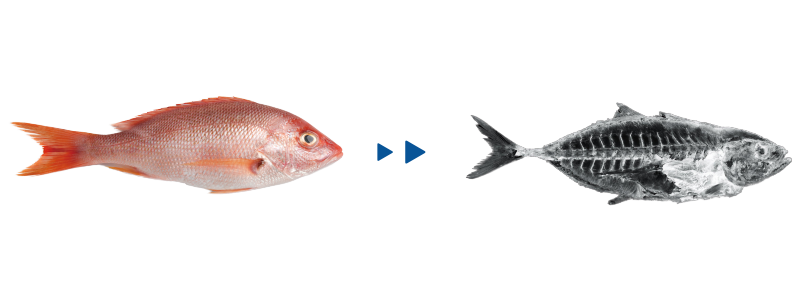
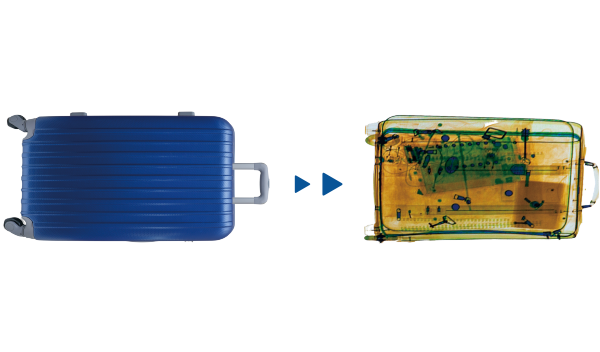
What would these artifacts and common items in life look like under the X-ray machine at the airport? Let's take a look at their internal structures or skeletons!
-
Koji Pottery "Thin Arhat"

-
Koji Pottery "Peace For All"

-
Luggage Case
-
Mobile Phone

-
Fish